Related Species: Fragrant Granadilla (Passiflora alata), Red Granadilla (P. coccinea), Maypop (P. incarnata), Yellow Granadilla (P. Laurifolia), Sweet Granadilla (P. ligularis), Sweet Calabash (P. maliformis), Banana Passion Fruit (P. mollissima), Giant Granadilla (P. quadrangularis).
Origin: The purple passion fruit is native from southern Brazil through Paraguay to northern Argentina. It has been stated that the yellow form is of unknown origin, or perhaps native to the Amazon region of Brazil, or is a hybrid between P. edulis and P. ligularis. Cytological studies have not borne out the hybrid theory. In Australia the purple passion fruit was flourishing and partially naturalized in coastal areas of Queensland before 1900. In Hawaii, seeds of the purple passion fruit, brought from Australia, were first planted in 1880 and the vine came to be popular in home gardens.
Adaptation: The purple passion fruit is subtropical and prefers a frost-free climate. However, there are cultivars that can take temperatures into the upper 20's (°F) without serious damage. The plant is widely grown in California as far north as San Jose, the Monterey Bay Area and the San Franciso Bay Area. The vines may lose some of their leaves in cool winters. The roots often resprout even if the top is killed. The plant does not grow well in intense summer heat. The yellow passion fruit is tropical or near-tropical and is much more intolerant of frost. Both forms need protection from the wind. Generally, annual rainfall should be at least 35 inches. Passion fruit vines make good container specimens but require maintenance. They perform well indoors.
Foliage: The evergreen leaves of passion fruit are alternate, deeply 3-lobed when mature and finely toothed. They are 3 to 8 inches long, deep green and glossy above, paler and dull beneath and, like the young stems and tendrils, tinged with red or purple, specially in the yellow form.
Flowers: A single, fragrant flower, 2 to 3 inches wide, is born at each node on the new growth. The bloom, clasped by 3 large, green, lifelike bracts, consists of 5 greenish-white sepals, 5 white petals and a fringelike corona of straight, white-tipped rays, rich purple at the base. It also has 5 stamens with large anthers, the ovary and triple-branched style forming a prominent central structure. Purple passion fruit is self-fruitful, but pollination is best under humid conditions. The flowers of the yellow form are perfect but self-sterile. Carpenter bees are the most efficient pollinator, much more so than honey bees. Wind is ineffective because of the heaviness and stickiness of the pollen. The flowers can also be hand pollinated.
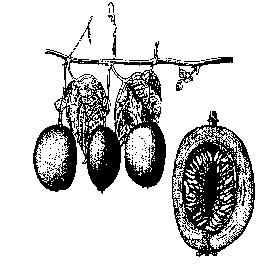
Fruit: The nearly round or ovoid fruit, 1-1/2 to 3 inches wide, has a tough rind that is smooth and waxy and ranging in hue from dark purple with faint, fine white specks, to light yellow or pumpkin-color. Within is a cavity more or less filled with an aromatic mass of double walled, membranous sacs containing orange-colored, pulpy juice and as many as 250 small, hard, dark brown or black, pitted seeds. The unique flavor is appealing, musky, guava-like and sweet/tart to tart. The yellow form has generally larger fruit than the purple, but the pulp of the purple is less acid, richer in aroma and flavor, and has a higher proportion of juice (35-38%). Numerous hybrids have been made between purple and the yellow passion fruit, often yielding colors and other characteristic intermediate between the two forms. The vine, especially the yellow form, is fast-growing and will begin to bear in 1 to 3 years. Ripening occurs 70 to 80 days after pollination.
Soil: Passion fruit vines grow on many soil types but light to heavy sandy loams with a pH of 6.5 to 7.5 are the most suitable. Excellent drainage is absolutely necessary. Also, the soil should be rich in organic matter and low in salts. If the soil is too acid, lime must be applied. Because the vines are shallow-rooted, they will benefit from a thick layer of organic mulch.
Irrigation: Regular watering will keep a vine flowering and fruiting almost continuously. Water requirement is high when fruits are approaching maturity. If the soil is dry, fruits may shrivel and fall prematurely.
Fertilization: Passion fruit vines are vigorous growers and require regular fertilizing. A good choice is 10-5-20 NPK applied at the rate of 3 pounds per plant 4 times a year. Too much nitrogen results in vigorous foliage growth at the expense of flowering. Passion fruit vines should always be watched for deficiencies, particularly in potassium and calcium, and of less importance, magnesium. Plants that have been damaged by frost should receive a generous fertilizing after the weather has warmed
Pruning: Pruning is necessary to keep the vines within bounds, to make harvest easier and to keep the plants productive by maintaining vigorous growth. In warm winter climates prune immediately after harvest. In areas with cool winters prune in early spring. As a a general rule remove all weak growth and cut back vigorous growth by at least one third. In very hot climates allow a thick canopy of foliage to grow around the fruit to prevent sunburn.
Frost Protection: Because of their mass, passion fruit vines are difficult to cover when freezes threaten, but the layers of leaves help protect the inner branches from frost damage. The plant will also usually come back even when frozen to the ground. The best strategy is to grow the vines against a wall or deck or in a patio. Any kind of overhead protection provides additional benefits.
Propagation: Passion fruit vines are usually grown from seeds. With the yellow form seedling variation provides cross-pollination and helps overcome the problem of self-sterility. Seed planted soon after removal from the fruit will germinate in 10 to 20 days. Cleaned and stored seeds have a lower and slower rate of germination. Seeds should be planted 1/2 to 1 inch deep in beds, and seedlings may be transplanted when 10 inches high. If taller (up to 3 feet), the tops should be cut back and the plants heavily watered.
Plants can also be propagated by layers or cuttings of matured wood with 3 to 4 nodes. Rooting may be hastened by hormone treatment. Cuttings should be well rooted and ready for setting out in 90 days. Grafting is an important means of perpetuating hybrids and reducing nematode damage and diseases by utilizing the resistant yellow passion fruit rootstock. Scions of healthy young plants are grafted to seedlings, making sure the diameter of the scion matches that of the rootstock. Either a cleft graft, whip graft or side-wedge graft may be made.
Pests and Diseases: In tropical areas passion fruit vines are attacked by a host of pests and diseases. In these areas the purple passion fruit is particularly susceptible to nematodes, while the yellow passion fruit is more nematode resistant. In California the problems are much less severe, although the plants can be afflicted with nematodes and viruses as well as Fusarium and other diseases that thrive in cool soils. Nematodes are partially responsible for the short life of many passion fruit vines. Snails can also be a serious problem in California, often completely stripping a vine of leaves and bark, killing young plants or predisposing them to disease.
Harvest: The fruit will quickly turn from green to deep purple (or yellow) when ripe and then fall to the ground within a few days. They can either be picked when they change color or gathered from the ground each day. To store passion fruit, wash and dry them gently and place them in bags. They should last 2 to 3 weeks at 50° F. The fruit is sweetest when slightly shriveled. Both the fruit and the juice freeze well. The flavor of passion fruit blends well with citrus and many other fruit flavors, and is quickly appreciated by many people as they become familiar with it.